
The CAP Theorem is a fundamental principle in distributed systems, stating that it is impossible for a system to simultaneously provide Consistency, Availability, and Partition Tolerance. The theorem often comes up in technical interviews to assess a candidate’s knowledge in designing distributed systems and handling their inevitable trade-offs. Clear understanding and application of the CAP theorem play a significant role when dealing with large-scale data processing and ensuring optimal system performance under various failure modes.
CAP Theorem Fundamentals
- 1.
What is CAP Theorem and why it’s important for distributed systems?
Answer:The CAP Theorem, proposed by Eric Brewer in 2000, serves as a fundamental principle for distributed systems. It postulates that of the three potential system attributes - Consistency, Availability, and Partition tolerance (known as “CAP”) - it’s impossible for a distributed system to simultaneously guarantee all three.
Visual Representation
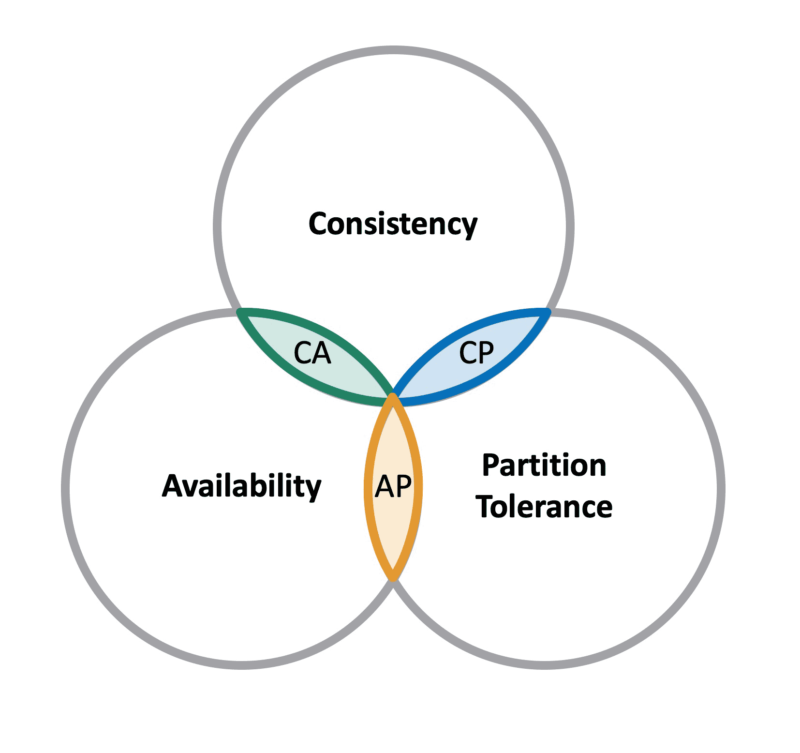
The Three Attributes
-
Consistency ©: All nodes in the system have the same data at the same time. Any data written to the system is immediately visible to all nodes.
-
Availability (A): Every request made to the system receives a response, either with the requested data or an error message.
-
Partition Tolerance (P): The system continues to operate – ensuring both C and A as defined above – despite network partitions (i.e., messages lost or the failure of part of the network).
In essence, while any two of the CAP triad are attainable, a distributed system cannot universally ensure all three attributes.
Understanding the Trade-offs
-
CP Systems: Emphasize Consistency and Partition Tolerance. These systems ace at safeguarding data integrity but may sacrifice availability during network partitions. Example: Most traditional RDBMS setups where data consistency is vital.
-
AP Systems: Prioritize Availability and Partition Tolerance, granting tolerance against network partitions but permitting temporary inconsistencies for high availability. Example: DynamoDB and other NoSQL databases that emphasize on high availability.
-
CA Systems: Ensure Consistency and Availability but do not commit to Partition Tolerance. These systems are often not considered true distributed systems because they can’t operate if the full network is not reachable. Example: Locally replicated databases where all instances are expected to maintain consistency.
CAP Theorem in Real-World Examples
-
Google’s Spanner: Balances between strong consistency and low latency using atomic clocks but not under network partitions.
-
Amazon’s DynamoDB: Ensures availability and performance at the expenses of strong consistency, offering tunable consistency levels for read operations.
-
Cassandra and Riak: Favored by distributed systems for their AP potential, especially in settings where availability and partition tolerance are crucial.
Why CAP Matters
Understanding the CAP theorem is foundational for the design, deployment, and operation of distributed systems. It helps in making informed decisions about the data store’s design, performance, and trade-offs, aligning with the specific needs of the application.
While it’s tempting to achieve the “Holy Grail” of a system that delivers on all three CAP attributes, in practice, prioritizing two may streamline the system’s potential issues and enhance its overall functionality.
-
- 2.
How does the CAP Theorem define consistency in the context of a distributed system?
Answer:In the context of distributed systems, consistency emphasizes that all nodes in the system reflect the most recent write to any part of the system.
The CAP theorem, however, suggests that in the presence of a network partition (P), a choice has to be made between availability and consistency.
This results in two main consistency models:
-
Eventual Consistency: Under this model, updates made to the system will propagate and reach all nodes eventually. While this means that the system may not immediately reflect the latest changes, it is still considered “consistent.”
-
Strong Consistency: Unlike eventual consistency, systems following strong consistency guarantee that all nodes will have the most recent version of data at all times. This approach prioritizes consistency over availability in the face of network partitions.
It’s important to note that while strong consistency provides powerful guarantees, it can lead to reduced availability during network partitions, making the system less resilient.
-
- 3.
What does availability mean in CAP Theorem?
Answer:Availability in the context of CAP theorem refers to the system’s ability to process and respond to user requests in a timely fashion, even when certain components or nodes within the system are faulty or unreachable.
A system that’s designed for high availability ensures that, despite errors or network partitions, it remains operational and capable of serving user requests to the best of its abilities.
The traditional shorthand for this principle, as coined by Eric Brewer, is as follows:
- CAP: It’s important for a system to strive for both consistency and partition tolerance. Yet, in real-world distributed systems, achieving absolute simultaneous consistency and partition tolerance might be impractical. As a result, design choices are often made to prioritize one of these properties over the other. The most common trade-off is between consistency and availability, leading to the well-established CAP theorem.
The standard analogy that captures the CAP theorem’s trade-offs is the situation of a network partition:
-
Consistency vs. Availability: Imagine a scenario where network segments are partitioned, and nodes in one segment are unable to communicate with nodes in another segment. In this situation, a system must choose to either maintain consistency and disallow writes ( and ) or remain available but allow for temporary inconsistencies (Possibly and ).
-
Equilibrium Point: With only one segment remaining reachable, a system essentially operates as a centralized or non-partition-tolerant system. Unclearly, it should compromise on availability () or consistency ().
-
Operating Beyond the Equilibrium Point: Struggling to stay consistent or available is a significant risk for distributed systems. In contrast, relaxing the consistency requirements (Possibly ) can sometimes reduce the complexity of ensuring liveliness. Ensuring partition tolerance during such scenarios is equally critical.
-
Consistency Models: The level of consistency that the system provides depends on its design and the chosen consistency mechanism. Different models, such as eventual consistency, causal consistency, or strong consistency, offer varying degrees of accuracy about the data.
The system’s architecture and the strategies it employs, like data partitioning, replication, and fault-tolerance mechanisms, significantly influence its capacity in balancing both consistency and availability.
- 4.
Explain partition tolerance in a distributed system as stated by the CAP Theorem.
Answer:Partition tolerance in the context of the CAP theorem refers to a distributed system’s ability to remain operational even when communication between system components (nodes) is partitioned or disrupted.
In other words, a Partition-Tolerant (P) system can maintain its functionality in the presence of network failures and communication breakdowns. This characteristic is particularly crucial for distributed systems that operate on unreliable networks, where occasional partitioning is an expected condition.
Core Concepts
-
Network Partitions: These occur when nodes within a distributed system are separated due to network issues, making communication between partitioned nodes difficult or impossible.
-
CAP Trade-offs: The CAP theorem highlights that due to practical design constraints, it’s not possible for a distributed system to simultaneously guarantee Consistency, Availability, and Partition Tolerance. Therefore, system designers must make trade-offs based on the specific requirements of their applications.
Examples
-
Real-time Collaboration Tools: Often prioritize Availability over Absolute Consistency. For example, in multi-user text editors like Google Docs, users might observe occasional “conflicts” in edited text.
-
Distributed Databases: Some distributed databases focus on Eventual Consistency and high Availability, especially during network partitions. They synchronize data across partitions after the network is restored.
-
Semi-Synchronous Replication: Systems employing a hybrid model might temporarily switch from strong consistency to eventual consistency during partition scenarios.
-
Geographically Distributed Systems: Systems functioning across multiple data centers or geographical regions are designed to handle network partitions for improved performance, fault tolerance, and disaster recovery.
Code Example: PACELC Theorem in Dynamo-Style Databases
Here is the code:
from datetime import datetime def get_timestamp(): return datetime.utcnow().timestamp() class DynamoDB: data = {} @staticmethod def get(key): return DynamoDB.data.get(key, {}).get('value') @staticmethod def put(key, value): timestamp = get_timestamp() DynamoDB.data[key] = {'value': value, 'timestamp': timestamp} @staticmethod def find_in_range(start, end): return {key: entry['value'] for key, entry in DynamoDB.data.items() if start <= entry['timestamp'] <= end}In this simplified example:
put()adds a key-value pair with a timestamp.get()retrieves the last value for a given key.find_in_range()finds values within a given timestamp range, which allows systems to merge data after a partition heals.
In a partitioned state:
# Node A DynamoDB.put('name', 'Alice') # Node B DynamoDB.put('name', 'Bob') DynamoDB.get('name') # Returns 'Bob' as it has the most recent timestampAfter the partition heals:
# Node A and Node B are now synchronized DynamoDB.get('name') # Can return either 'Alice' or 'Bob' based on the last update. -
Real-World Implications and Trade-offs
- 5.
Give an example of a real system that favors consistency over availability.
Answer:A notable example of a real system that prioritizes Consistency over Availability is relational databases like MySQL or PostgreSQL in their default configuration.
Whenever these databases encounter network partitions or service failures, they tend to favour data consistency even if it means sacrificing availability, making them an apt match for organizations where data integrity is non-negotiable.
Code example:
SELECTfrom MySQL leading AP system in a CP stanceHere is the SQL query code:
-- Retrieve the latest loan record for user with ID 108 and limit the result to one record SELECT * FROM loan_information WHERE user_id = 108 ORDER BY loan_date DESC LIMIT 1;In this scenario, MySQL might fail to respond to some client requests if it cannot guarantee consistency across all its nodes.
When to Use Consistency Over Availability
- Banking Systems: They require absolute data consistency, especially when handling transactions or managing account information.
- E-commerce Platforms: During flash sales or when stock is running low, it’s critical to prevent overselling to ensure the displayed product quantity is accurate.
- Data-Integrity-Critical Applications: Systems where any data corruption could have severe repercussions, such as those managing sensitive personal or health-related information.
- 6.
Can you name a system that prefers availability over consistency?
Answer:A system that favors availability over strong consistency belongs to the “AP” side of the CAP theorem.
Such systems aim to remain operational and respond to client requests, even if there are potential data inconsistencies across distributed components.
Apache Cassandra
Apache Cassandra is a prime example of an “AP” system that emphasizes high availability and partition tolerance, compromising logical consistency.
Core Design Principles
- Peer-to-Peer Structure: Nodes collaborate equally, without centralized control.
- Tunable Consistency: Administrators can adjust levels of consistency based on deployment needs.
- Distributed Hash Table (DHT): Utilizes consistent hashing and replication for efficient data distribution and fault tolerance.
Code Example: Setting Consistency Level in Cassandra
Here is the Java code:
import com.datastax.driver.core.ConsistencyLevel; import com.datastax.driver.core.Session; import com.datastax.driver.mapping.Mapper; // Establish the Cassandra database session Session session = ... // Create a mapper for the desired Entity class Mapper<MyEntity> myEntityMapper = new MappingManager(session).mapper(MyEntity.class); // Set the desired Consistency Level for the operation myEntityMapper.setDefaultSaveOptions(Mapper.Option.consistencyLevel(ConsistencyLevel.QUORUM)); - 7.
What is meant by “eventual consistency” in the context of CAP Theorem?
Answer:In the context of the CAP Theorem, “eventual consistency” means that given time without further updates, all replicas or nodes in a distributed system will reach a consistent state.
This consistency model doesn’t require a system to immediately reflect all changes to all nodes and enables system operations to proceed even if some replicas can’t be reached or are temporarily offline.
Eventual consistency guarantees:
- Liveness: The system continues to make progress.
- Safety Under Quorum: Consistency is ensured as long as operations are handled by a sufficient number of nodes.
- Resolved Conflicts: When two nodes present conflicting updates, after their eventual reconciliation, a consistent state emerges.
Global States in Eventual Consistency
The journey to consistency doesn’t follow a global clock. Instead, it unfolds at a local level. Each node, or groups of nodes, evolves toward consistency independently.
Resolving Conflicts
It’s crucial for systems designed with eventual consistency to have conflict resolution mechanisms. These ensure disparate updates, which occurred in isolation, are later integrated in a coherent manner.
Example: Amazon Shopping Cart
Imagine you and a friend both add the last available item to your Amazon shopping carts at the same time. A system designed with eventual consistency might initially allow both actions. However, upon checkout, the system notices the conflict and triggers a resolution, ensuring only one cart can complete the purchase.
Potential Concerns
- Complexities in Development: Crafting systems with adequate conflict resolution can be intricate.
- Hazards of Stale Data: As updates can take time to propagate, users may view outdated information.
- Uncertain Termination: Until all nodes are consistent, there’s no absolute certainty that the system has reached a stable state.
Code Example: Eventual Consistency
Here is the Python code:
class ShoppingCart: def __init__(self): self.items = [] def add_item(self, item): self.items.append(item) def remove_item(self, item): if item in self.items: self.items.remove(item) def checkout(self): # Simulating eventual consistency time.sleep(1) if len(self.items) == 0: print("Checkout successful!") else: print("Checkout failed due to inconsistency. Please try again.") - 8.
What trade-offs you might have to make in a distributed system design due to the CAP Theorem.
Answer:The CAP theorem, also known as Brewer’s theorem, places constraints on distributed systems. As per the theorem, a system can guarantee at most two out of three characteristics: Consistency, Availability, and Partition tolerance.
Let’s look in detail at the trade-offs and system design considerations for distributed databases in view of CAP theorem.
1. CP Systems: Consistency and Partition Tolerance
- Characteristics
- Consistency: All nodes in the system have the most recent data copy. Any read or write operation occurs on the most recent data.
- Partition Tolerance: The system continues to function despite network partitions or lost messages.
- Trade-offs
- These systems potentially become unavailable if they cannot confirm that a majority of nodes have been reached. This is inherently a part of being partition tolerant. The system will refuse operations that it cannot guarantee as complete. The primary use case for these systems is in situations where data integrity is crucial and can outweigh temporarily lost availability.
- Real-world Examples: - Most traditional RDBMS configurations with primary-replica setups lean towards this model. In the context of specific databases, technologies like MongoDB or Apache HBase can be tweaked to exhibit these characteristics by adjusting the number of nodes that constitute a primary shard.
2. AP Systems: Availability and Partition Tolerance
- Characteristics
- Availability: The system ensures that all write and read requests receive a response, even in the face of network difficulties or the loss of a subset of nodes.
- Partition Tolerance: The system will continue to operate despite network partitions or message loss.
- Trade-offs
- These systems can potentially sacrifice consistency in favor of availability. In other words, at any given point in time, different nodes might have or return different views of the data.
- Real-world Examples: - Databases like Couchbase or Cassandra are inherently designed to provide availability over strict consistency.
3. CP vs AP Scenarios: Making the Right Design Choice
- Business Considerations:
- Businesses where data accuracy is top priority, like financial institutions or scientific research labs, would favor systems of strong consistency (CP systems). Conversely, systems handling heavy user loads and real-time data are more likely to seek availability and performance, making AP systems a better fit.
- Middle Grounds: Several databases implement mechanisms to balance these extremes, offering tunable consistency settings. For example, DynamoDB and Riak furnish users with control over certain consistency parameters, catering to varying application needs.
- Dynamic Choice:
- Some systems adapt their consistency and availability modes in response to changing factors like network speed and latency. Techniques like eventual consistency and quorum reads allow systems such as Riak and Cassandra to navigate between CP and AP characteristics as the situation demands.
Designing with CAP in Mind
- 9.
How would you design a system that requires high availability and what trade-offs would you have to make according to the CAP Theorem?
Answer:When designing a distributed system that requires high availability, you are primarily focusing on ensuring that the system can continue to provide a reliable service in the presence of failures. However, striving for high availability inevitably leads to trade-offs in terms of both consistency and partition tolerance, which are fundamental concepts in the CAP Theorem.
Theoretical Background: CAP Theorem Implications
Systems that emphasize high availability and partition tolerance while relaxing strict consistency are commonly termed as AP systems (Availability and Partition tolerance systems). These systems usually maintain a form of eventual consistency, which means that the data will become consistent over time.
Key Characteristics of AP systems
- Primary Focus: High availability and continued operations in the face of network partitions.
- Consequence: Temporary inconsistencies in data, which are resolved over time.
- Examples: Apache Cassandra, Riak, DynamoDB.
Trade-Offs
- Consistency: Eventual consistency is typically aimed for, where all replicas of the data will converge, but there might be temporary inconsistencies.
- Availability: The system will prioritize serving read and write operations, even in the presence of failures or when certain nodes are inaccessible.
- Partition Tolerance: The system will strive to remain operational even when network partitions occur.
- 10.
If a system is experiencing a partition (network failure), what strategies can you employ to maintain service?
Answer:When a distributed system experiences network partitions, ensuring consistency, availability, and partition tolerance can be challenging. However, certain strategies can help the system maintain its functions.
CAP during Partition
Network partitions force distributed systems to choose between consistency and availability. Let’s look at the strategies, also known as Brewer’s Conjecture, that help systems handle this delicate balance.
CAP Strategies
-
CA Pattern: Opt for consistency and availability during network partitions. Resume normal operations when the network is stable.
-
CP Pattern: Prioritize consistency over availability. The system might have to be slower, respond with errors, or go offline altogether when a partition occurs.
-
AP Pattern: In case of partition, focus on availability over strict consistency. The system continues to serve requests but might return divergent versions of the data on either side of the partition.
Code Example: Consistency over Availability
Here is the Python code:
def read_data_from_node(node, data_store): try: data = data_store[node].read() return data except NetworkError: # Log the error or handle it, and possibly retry pass def read_from_replicas(replica_nodes, data_store): for node in replica_nodes: data = read_data_from_node(node, data_store) if data: return data # If none of the replicas returned valid data raise UnavailableException("None of the replicas returned valid data") # Usage: try: data = read_from_replicas(replica_nodes, data_store) process_data(data) except UnavailableException: fallback_to_local_cache()In this example, when reading from replicas in a CP system, it prioritizes consistency but ensures that the system remains available, falling back to a local cache if needed.
-
- 11.
Considering the CAP Theorem, how would you approach building a distributed system that handles sensitive financial transactions?
Answer:When dealing with sensitive financial transactions, it’s crucial to consider the CAP (Consistency, Availability, Partition Tolerance) theorem to ensure the system’s integrity and reliability. Here is a summary of the CAP theorem:
-
Consistency: All nodes in the system have the same data at the same time.
-
Availability: Every request gets a response, either with the requested data or an error message.
-
Partition Tolerance: The system continues to operate even when network partitions occur.
Essential Considerations
Sensitivity to CAP Components
While all three components are important, in a financial system, maintaining consistency is critical, since data integrity is paramount. Therefore, the system should not relax on consistency for the sake of high availability or partition tolerance.
Latency vs. Freshness
In a distributed system, data transmission speed across nodes can vary, leading to different latencies in data updates. The challenge is to balance the need for real-time data updates with the potential latency across distributed nodes.
Mechanisms for Recovery
Robust error-recovery mechanisms should be in place to ensure data consistency across nodes, primarily after network partitions.
Data Synchronization Methods
Consistency with Strong Server-Driven Data Management
- Direct Client-Server Communication: This approach ensures data consistency and allows the server to validate incoming data. For efficiency in financial systems, it’s important to minimize unnecessary writes, especially if the data doesn’t need to be regularly updated, using techniques such as caching and batching.
Asynchronous Replication Methods
-
Write-Ahead Log (WAL): One common method of ensuring consistent, distributed data updates is through WAL, where write operations are queued and then executed in the same order on all nodes.
-
Quorum-based Mechanisms: Implement ing a majority-rules system can ensure that a data update gets acknowledged by a majority of nodes before it is considered successful, maintaining data integrity.
Code Example: Quorum-based Mechanism
Here is the Java code:
public class QuorumBasedConsistency { private Map<Node, boolean> acks = new HashMap<>(); private boolean isQuorumReached() { int ackCount = acks.values().stream().filter(ack -> ack).count(); return ackCount > acks.size() / 2; } public synchronized void initiateDataUpdate(Data data) { acks.clear(); for (Node node : connectedNodes) { sendUpdateRequest(node, data); } } public synchronized void recordAcknowledge(Node node) { acks.put(node, true); if (isQuorumReached()) { commitDataUpdate(); } } } -
CAP in Practice
- 12.
Describe a scenario where a system may switch from being CA to AP during its operation due to external factors.
Answer:A CAP Theorem analysis reveals that it’s challenging for a distributed system to simultaneously guarantee all three of the following:
- Consistency (every read receives the most recent write or an error)
- Availability (every request receives a response, without guarantee of data consistency)
- Partition Tolerance (the system operates despite network failures)
Use-Case: E-Commerce Platform
Initially, the shopping cart service on an e-commerce platform operates in a CA (Consistent and Available) mode. Upon detecting network issues, the system transitions to an AP (Available and Partition-Tolerant) configuration.
CA Mode
-
Consistency: When a user adds an item to their cart and performs a subsequent query, they receive the most recent data without the risk of outdated or conflicting information. The system employs strong consistency mechanisms like two-phase commit or serializable transactions.
-
Availability: Users, under normal conditions, consistently interact with the service. Any request made to the system delivers an immediate response, ensuring the service is available.
-
Partition Tolerance: The system’s ability to operate during potential network partitions isn’t the primary concern here.
AP Mode
-
Consistency: The service temporarily relaxes its consistency models to ensure that it remains available at the expense of delivering potentially inconsistent data. For instance, in the cache, writes might be performed asynchronously, leading to a period where the most recent write isn’t reflected.
-
Availability: The service guarantees that every non-failing request receives a response. The focus here is on remaining accessible despite those network hiccups that can cause partitions.
-
Partition Tolerance: The service adapts to the detected partition, modifying its operations to continue serving user requests, even if that means making compromises in consistency guarantees.
- 13.
How do quorums help in achieving consistency or availability in distributed systems, and how is this related to CAP Theorem?
Answer:In distributed systems, quorums enable trade-offs between strong consistency and high availability. This is closely related to CAP theorem which states that it’s not possible for a distributed system to always guarantee all three of the following simultaneously:
- Consistency (all nodes see the same data)
- Availability (every request receives a response, not an error)
- Partition Tolerance (the system continues to operate despite arbitrary message loss or failure of part of the network)
While not intuitive at first, the use of quorums for data operations makes the relationships between CAP components clearer. Quorum-based systems partition data into subsets, and operations must gather agreement from a certain number of subsets to proceed.
A read quorum is the minimum number of nodes that need to agree when reading data, while a write quorum is the minimum number needed for writing/modifying data. The balance between these two quorums influences the system’s CP or AP characteristics.
CAP Theorem and Quorum Systems: A Trade-Off
-
Quorum for Strong Consistency: A high-read and high-write quorum can ensure that recent writes are visible to subsequent reads, ensuring strong consistency at the possible expense of availability during network partitions.
-
Quorum for High Availability: Reducing the quorum requirements for reads and writes prioritizes availability by potentially allowing conflicting writes.
Code Example: Significance of Quorums in Distributed Databases
Here is the Python code:
from typing import List, Set # Example of distributed set using quorums class DistributedSet: def __init__(self, nodes: List[str], read_quorum: int, write_quorum: int): self.nodes = nodes self.read_quorum = read_quorum self.write_quorum = write_quorum # Reads the set using a defined read quorum def read(self) -> Set: results = self.read_from_quorum() if self.is_quorum_achieved(results, self.read_quorum): return self.process_data(results) # Writes to the set using a defined write quorum def write(self, item): write_results = self.write_to_quorum(item) if self.is_quorum_achieved(write_results, self.write_quorum): return True # Reads data from nodes and returns a set of results def read_from_quorum(self) -> Set: pass # Implement as per the distributed system settings # Writes data to nodes and returns a set of write acknowledgements def write_to_quorum(self, item): pass # Implement as per the distributed system settings # Verifies if a quorum is met using the results and the required threshold def is_quorum_achieved(self, results: Set, threshold: int) -> bool: return len(results) >= threshold # Processes the data received and constructs a set def process_data(self, results: Set) -> Set: return set(results) - 14.
How do modern databases like Cassandra or DynamoDB address the challenges posed by the CAP Theorem?
Answer:While it’s impossible for any distributed system to simultaneously guarantee consistency, availability, and partition tolerance due to the CAP Theorem, modern databases like Cassandra and DynamoDB offer robust ways to manage these trade-offs.
Cassandra
Key Architectural Features
- Consistency and Partition Tolerance: Utilizes a tunable consistency model to navigate the consistency-partition tolerance spectrum.
- Availability and Partition Tolerance: Remains available even in the presence of network partitions, thanks to its decentralized, masterless architecture.
Key Mechanisms
- Quorum-Based Consistency: By default, it requires a majority of replicas to acknowledge for read and write operations, ensuring strong consistency in a multi-datacenter setup. However, this mechanism can be adjusted for lower latency at the cost of consistency.
- Tunable CAP: Offers configurable levels of consistency for reads and writes.
DynamoDB
Key Architectural Features
- Consistency and Partition Tolerance: Offers two consistency models - eventual consistency and strong consistency - that can be selected based on application-specific requirements.
- Availability and Partition Tolerance: Prioritizes fault tolerance and remains highly available unless the whole system becomes partitioned.
Key Mechanisms
- Primary Key Consistency: Its partitioning mechanism ensures that consistent reads and writes are guaranteed within the same partition (i.e., using the same primary key).
- Configurable Consistency: Provides a means for developers to choose the desired consistency level for read operations.
Conclusion
Both Cassandra and DynamoDB exemplify nuanced ways modern databases navigate the CAP trade-offs, offering a spectrum of options for users to tailor their systems.
Advanced Understanding of CAP
- 15.
Explain how concepts like idempotency, commutativity, and convergence are important in designs that are influenced by the CAP Theorem.
Answer:In distributed systems, conformity with the CAP Theorem often leads to the use of strategies emphasizing commutativity, idempotence, and eventual consistency. Let’s see how these concepts play a vital role.
Practical Applications
-
RESTful Systems: REST API methods that are idempotent and commutative, like
PUT, seamlessly fit the principles of the CAP theorem. -
State-Based Systems: Commutativity and idempotence support eventual consistency by enabling systems to accept and align states.
-
Conflict Resolution Mechanisms: Often based on commutativity and idempotence of operations, these mechanisms help in situations where multiple parties modify the same resource.
-
Caching Strategies: Idempotent operations are more cacheable, enhancing performance. Caches propagate the latest values for keys, ensuring approximate convergence.
Code Example: Idempotency and Commutativity
Here is the Python code:
class Counter: def __init__(self): self.value = 0 def increment_safe(self): # Idempotent and commutative operation self.value += 1 def assert_state(self, expected_value): # Asserting state remains consistent despite any re-applications assert self.value == expected_value # Example Usage counter = Counter() counter.increment_safe() counter.increment_safe() # assert_state should pass since increment is idempotent counter.assert_state(1) -